Any aspiring entrepreneur researching how to start a business will likely be advised to write a business plan. But few resources provide business plan examples to really guide you through writing one of your own.
Here are some real-world and illustrative business plan examples to help you craft your business plan.
7 business plan examples: section by section
The business plan examples in this article follow this example template:
- Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business.
- Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists.
- Market analysis. Research-based information about the industry and your target market.
- Products and services. What you plan to offer in exchange for money.
- Marketing plan. The promotional strategy to introduce your business to the world and drive sales.
- Logistics and operations plan. Everything that happens in the background to make your business function properly.
- Financial plan. A breakdown of your numbers to show what you need to get started as well as to prove viability of profitability.
Executive summary
Your executive summary is a page that gives a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. It’s easiest to save this section for last.
In this free business plan template, the executive summary is four paragraphs and takes a little over half a page:
Company description
You might repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, social media profile pages, or other properties that require a boilerplate description of your small business.
Soap brand ORRIS has a blurb on its About page that could easily be repurposed for the company description section of its business plan.

You can also go more in-depth with your company overview and include the following sections, like we did for Paw Print Post:
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your business—as an LLC, sole proprietorship, corporation, or other business type. “Paw Print Post will operate as a sole proprietorship run by the owner, Jane Matthews.”
- Nature of the business. “Paw Print Post sells unique, one-of-a-kind digitally printed cards that are customized with a pet’s unique paw prints.”
- Industry. “Paw Print Post operates primarily in the pet industry and sells goods that could also be categorized as part of the greeting card industry.”
- Background information. “Jane Matthews, the founder of Paw Print Post, has a long history in the pet industry and working with animals, and was recently trained as a graphic designer. She’s combining those two loves to capture a niche in the market: unique greeting cards customized with a pet’s paw prints, without needing to resort to the traditional (and messy) options of casting your pet’s prints in plaster or using pet-safe ink to have them stamp their ‘signature.’”
- Business objectives. “Jane will have Paw Print Post ready to launch at the Big Important Pet Expo in Toronto to get the word out among industry players and consumers alike. After two years in business, Jane aims to drive $150,000 in annual revenue from the sale of Paw Print Post’s signature greeting cards and have expanded into two new product categories.”
- Team. “Jane Matthews is the sole full-time employee of Paw Print Post but hires contractors as needed to support her workflow and fill gaps in her skill set. Notably, Paw Print Post has a standing contract for five hours a week of virtual assistant support with Virtual Assistants Pro.”
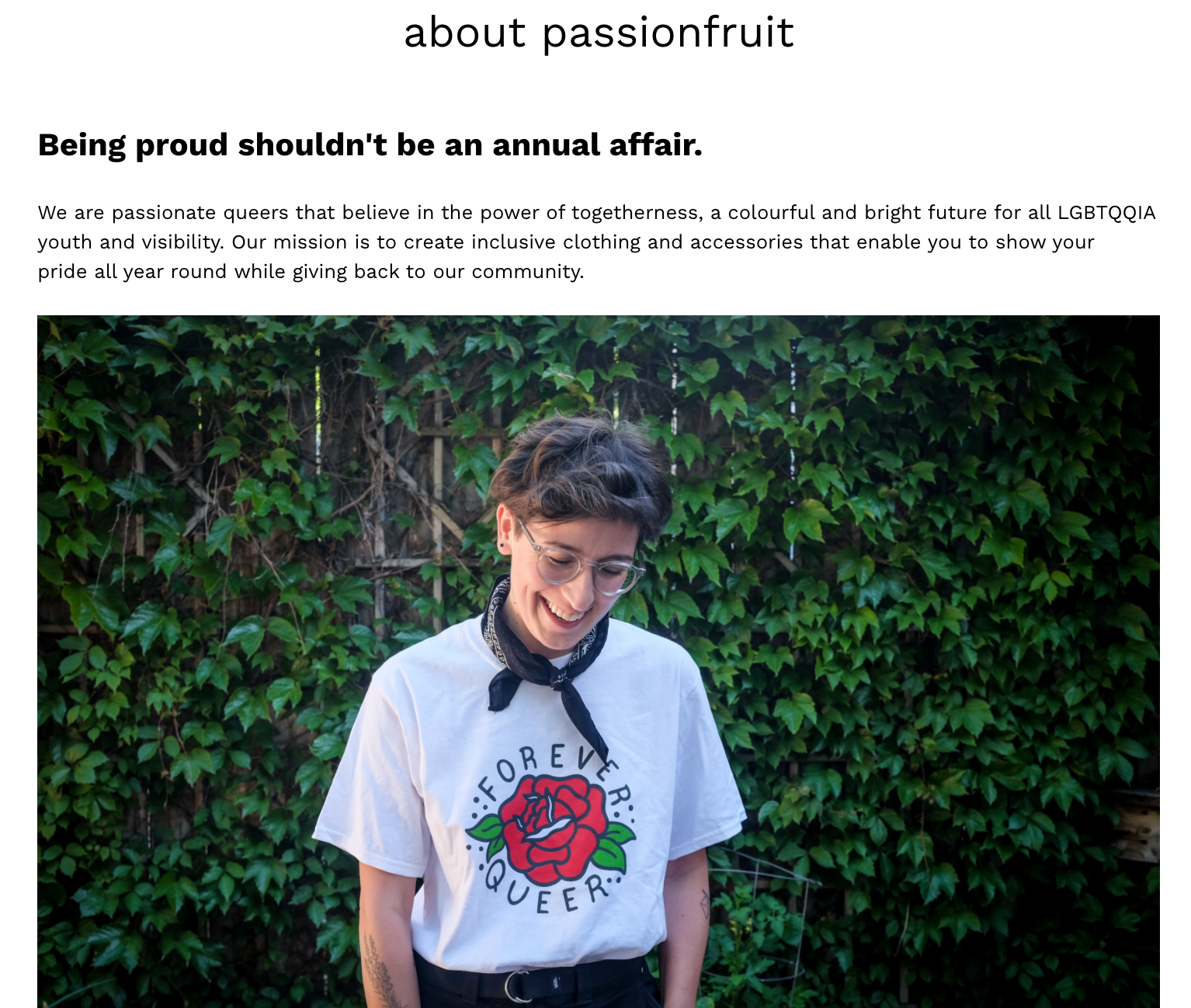
Your mission statement may also make an appearance here. Passionfruit shares its mission statement on its company website, and it would also work well in its example business plan.
Market analysis
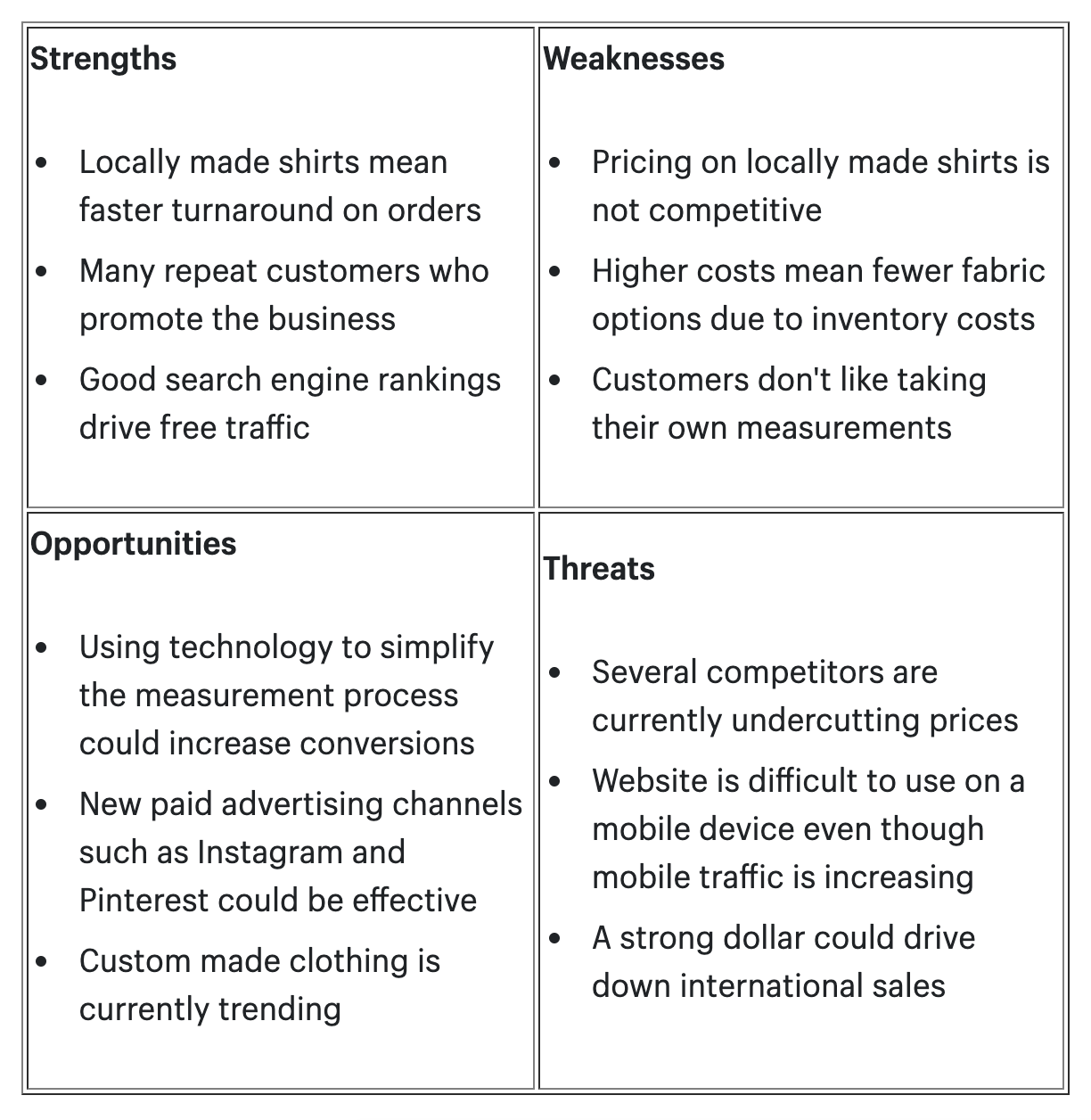
The market analysis consists of research about supply and demand, your target demographics, industry trends, and the competitive landscape. You might run a SWOT analysis and include that in your business plan.
Here’s an example SWOT analysis for an online tailored-shirt business:
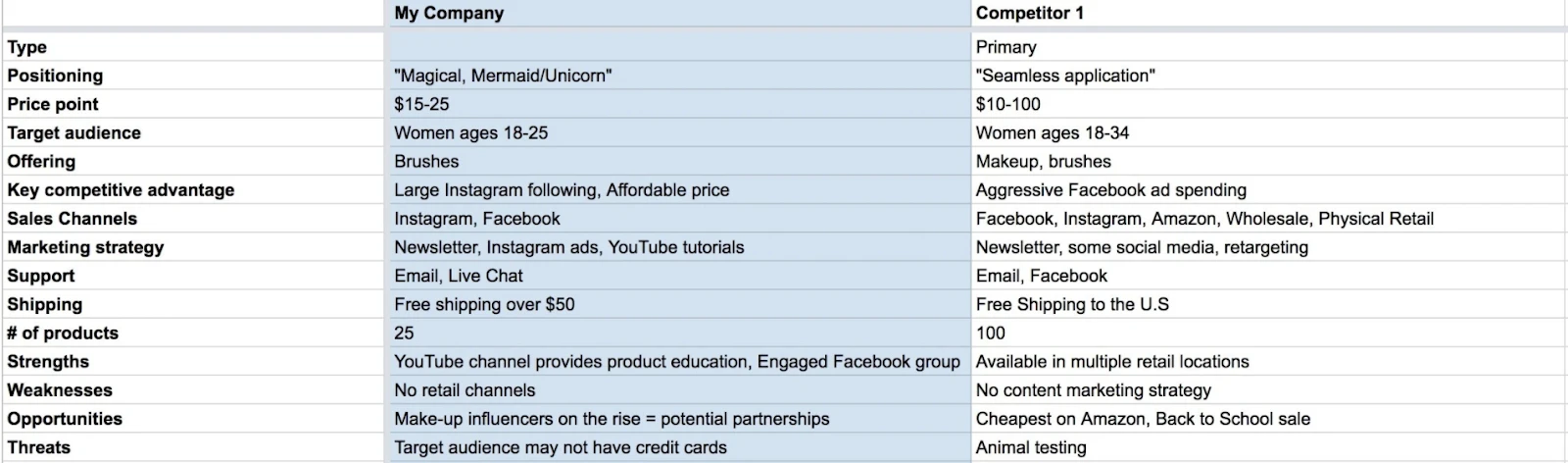
You’ll also want to do a competitive analysis as part of the market research component of your business plan. This will tell you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to differentiate your brand. Your competitive advantage audit might look like this:
Products and services
This section of your business plan describes your offerings—which products and services do you sell to your customers? Here’s what we wrote for Paw Print Post:

Marketing plan
It’s always a good idea to develop a marketing plan before you launch your business. Your marketing plan shows how you’ll get the word out about your business, and it’s an essential component of your business plan as well.
For Paw Print Post, we focused on four Ps: price, product, promotion, and place. However, you can take a different approach with your marketing plan. Maybe you can pull from your existing marketing strategy, or maybe you break it down by the different marketing channels. Whatever approach you take, your marketing plan should describe how you intend to promote your business and offerings to potential customers. It’s OK to go high level here.
Logistics and operations plan
For Paw Print Post, we looked at suppliers, production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
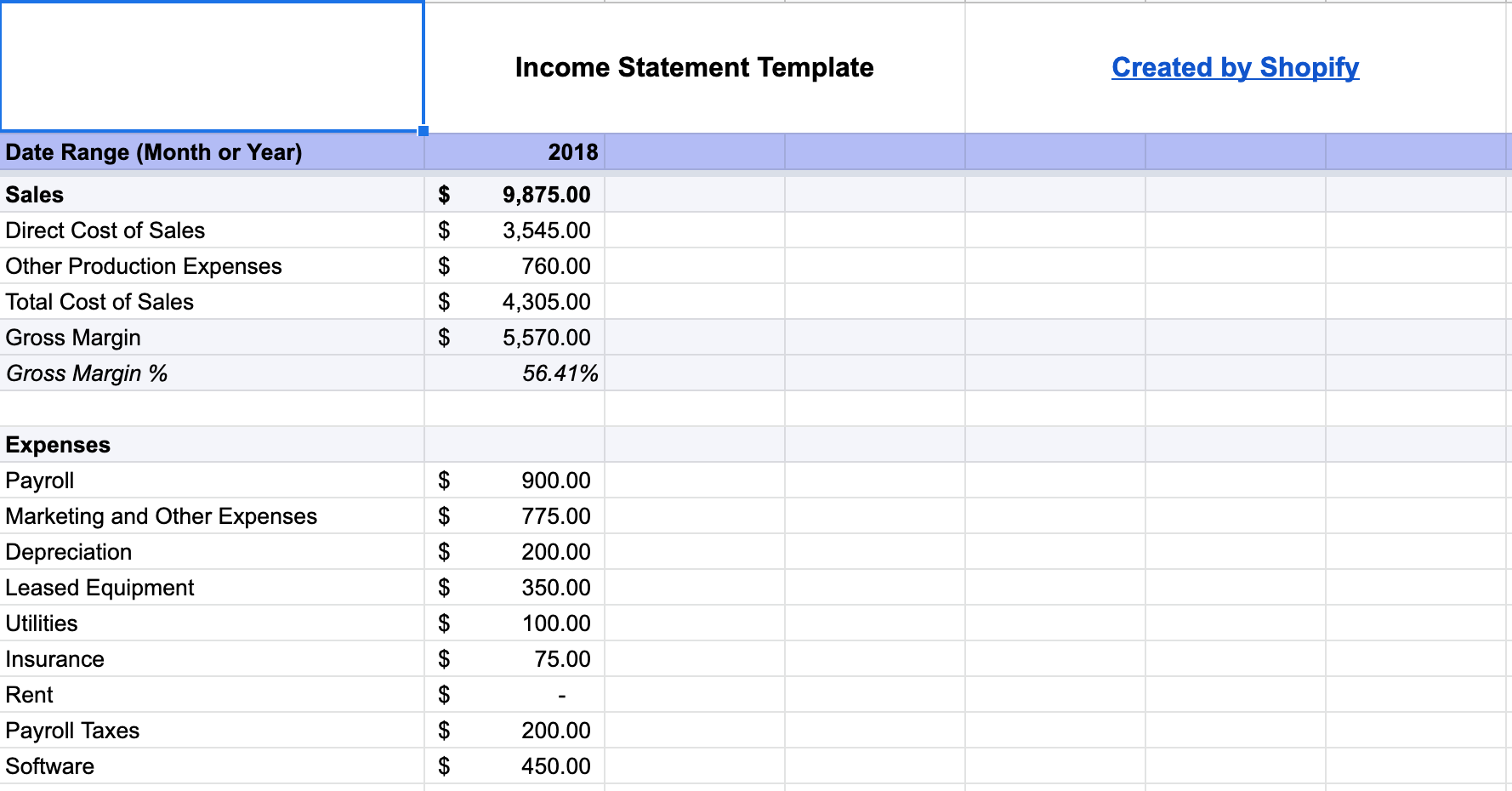
Financial plan
The financial plan provides a breakdown of sales, revenue, profit, expenses, and other relevant financial metrics related to funding and profiting from your business.
Ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy’s financial plan breaks down predicted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.
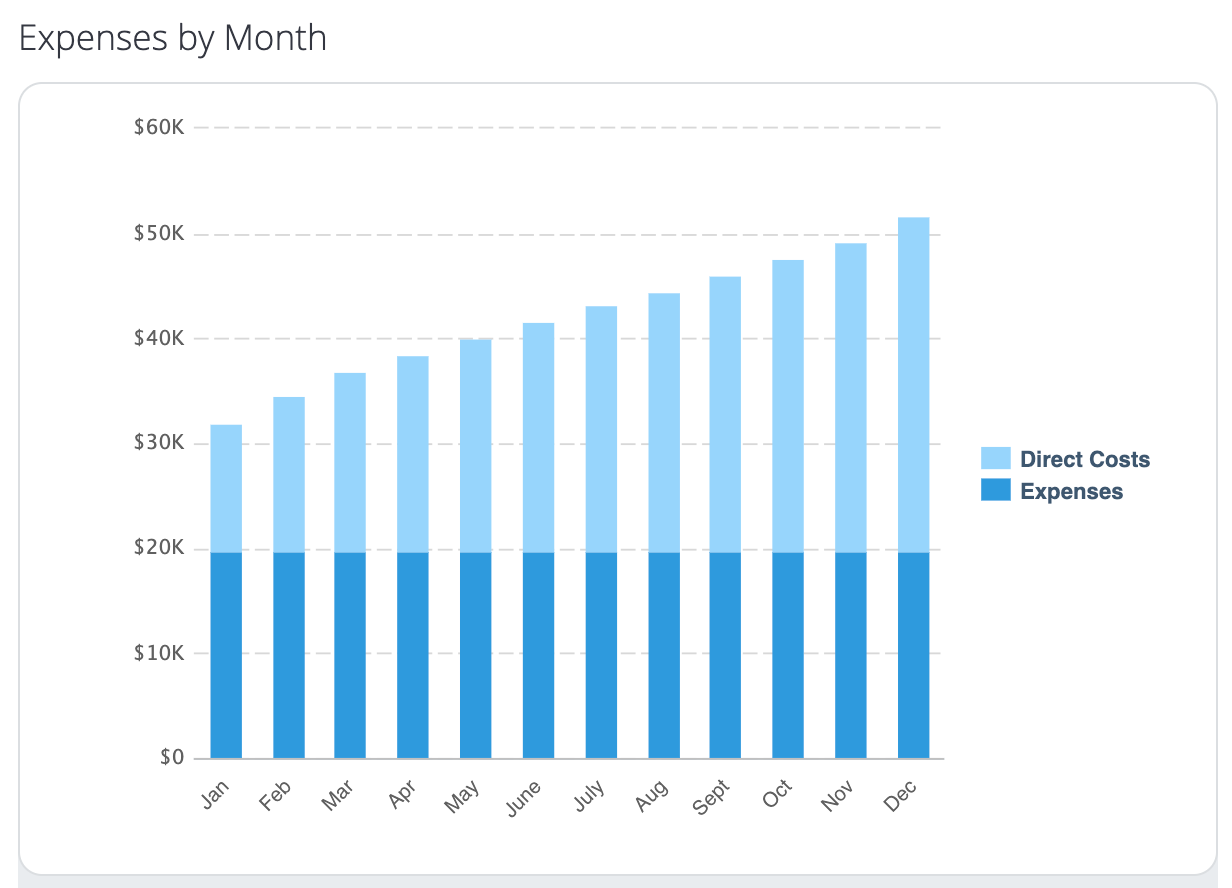
It then dives deeper into the financials to include:
- Funding needs
- Projected profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Projected cash-flow statement
You can use this financial plan spreadsheet to build your own financial statements, including income statement, balance sheet, and cash-flow statement.
Types of business plans, and what to include for each
One-pager
A one-page business plan is meant to be high level and easy to understand at a glance. You’ll want to include all of the sections, but make sure they’re truncated and summarized:
- Executive summary: truncated
- Market analysis: summarized
- Products and services: summarized
- Marketing plan: summarized
- Logistics and operations plan: summarized
- Financials: summarized
Startup
A startup business plan is for a new business. Typically, these plans are developed and shared to secure outside funding. As such, there’s a bigger focus on the financials, as well as on other sections that determine viability of your business idea—market research, for example.
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market analysis: in-depth
- Products and services
- Marketing plan
- Operations
- Financials: in-depth
Internal
Your internal business plan is meant to keep your team on the same page and aligned toward the same goal.
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market analysis
- Products and services
- Marketing plan
- Logistics and operations plan
- Financials
Strategic
A strategic, or growth, business plan is a bigger picture, more-long-term look at your business. As such, the forecasts tend to look further into the future, and growth and revenue goals may be higher. Essentially, you want to use all the sections you would in a normal business plan and build upon each.
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market analysis: comprehensive outlook
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Marketing plan: comprehensive outlook
- Logistics and operations plan: comprehensive outlook
- Financials: comprehensive outlook
Feasibility
Your feasibility business plan is sort of a pre-business plan—many refer to it as simply a feasibility study. This plan essentially lays the groundwork and validates that it’s worth the effort to make a full business plan for your idea. As such, it’s mostly centered around research.
- Company description
- Market analysis
- Products and services
- Logistics and operations plan
- Financials
More resources for validating your ideas:
Set yourself up for success as a business owner
Building a good business plan serves as a roadmap you can use for your ecommerce business at launch and as you reach each of your business goals. Business plans create accountability for entrepreneurs and synergy among teams, regardless of your business model.
Kickstart your ecommerce business and set yourself up for success with an intentional business planning process—and with the sample business plans above to guide your own path.
Business plan examples FAQ
How do I write a simple business plan?
To write a simple business plan, begin with an executive summary that outlines your business and your plans. Follow this with sections detailing your company description, market analysis, organization and management structure, your product or service, marketing and sales strategy, and financial projections. Each section should be concise and clearly illustrate your strategies and goals.
What is the best format to write a business plan?
The best business plan format presents your plan in a clear, organized manner, making it easier for potential investors to understand your business model and goals. Always begin with the executive summary and end with financial information or appendices for any additional data.
What are the 4 key elements of a business plan?
- Executive summary: A concise overview of the company’s mission, goals, target audience, and financial objectives.
- Business description: A description of the company’s purpose, operations, products and services, target markets, and competitive landscape.
- Market analysis: An analysis of the industry, market trends, potential customers, and competitors.
- Financial plan: A detailed description of the company’s financial forecasts and strategies.
What are the 3 main points of a business plan?
- Concept: Your concept should explain the purpose of your business and provide an overall summary of what you intend to accomplish.
- Contents: Your content should include details about the products and services you provide, your target market, and your competition.
- Cashflow: Your cash flow section should include information about your expected cash inflows and outflows, such as capital investments, operating costs, and revenue projections.


